Such decisions are usually based on past estimates and market research regarding the demand for products that are offered by the business. CVP Analysis helps the business in determining how much they need to sell to break even, i.e., no profit, no loss. Cost Volume Profit Analysis includes the analysis of sales price, fixed costs, variable costs, the number of goods sold, and how it affects the profit of the business. The aim of a company is to earn a profit, and profit depends upon a large number of factors, most notable among them is the cost of manufacturing and the volume of sales.
Identifying Sales Price in Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
We can then calculate the Break-even point using the formulas we discussed above. We know where Fixed Costs come from, now let us look at the contribution margin. Today we will take a look at Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis and the Break-even point (BEP) in sales. Using a tool like Google Sheets or Excel together with Layer can make your life much easier. Quickly connect your data sources and set up automatic updates to ensure updated data for your whole team.
Cost Volume Profit (CVP) Chart: Analysis & Example
You can also calculate your margin of safety to determine how far your sales can drop and you still break even. Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales volume, such as rent, salaries, and insurance. Impractical to assume sales mix remain constant since this depends on the changing demand levels. CVP simplifies the computation of breakeven in break-even analysis, and more generally allows simple computation of target income sales. It simplifies analysis of short run trade-offs in operational decisions.
- Follow the instructions to calculate the total contribution margin and the contribution margin per unit.
- This can be answered by finding the number of units sold or the sales dollar amount.
- CVP analysis, in short, enables establishing relationship between cost, volume of products, and profit margin.
- This includes challenges for CVP analysts when identifying what should be considered a fixed cost and what should be classified as a variable cost.
- On a per unit basis, the contributionmargin for Video Productions is $8 (the selling price of $20 minusthe variable cost per unit of $ 12).
Understanding Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
To learn about what-if analysis, as well as how to do it in Google Sheets, check out our related article on How To Perform What-If Analysis in Google Sheets. With CVP Analysis information, the management can better understand the overall performance and determine what units it should sell to break even or to reach a certain level cash payment or cash disbursement journal calculation of profit. These are simplifying, largely linearizing assumptions, which are often implicitly assumed in elementary discussions of costs and profits. In more advanced treatments and practice, costs and revenue are nonlinear, and the analysis is more complicated, but the intuition afforded by linear CVP remains basic and useful.
ChartExpo Survey
When carrying out CVP analysis, it’s important to remember that it makes certain key assumptions that don’t necessarily reflect reality, at least in the long term. The margin of safety shows you how much your sales can drop while still allowing your company to break even. To find the margin of safety, simply subtract the break-even amount for sales from the actual sales for your company. The analysis is restricted to the relevant range specified and beyond that the results can become unreliable. In a real-world example, the founder of Domino’s Pizza, Tom Managhan, faced an early problem involving poorly calculated CVP in his book “Pizza Tiger”.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis- Explained With Examples
This lets you work in the comfort of Microsoft Excel with the support of a much more sophisticated but intuitive data management system. Like all analytical methodologies, CVP analysis has inherent limitations. Learn how to run multiple regressions in Excel to analyze variable interactions, identify patterns, & enhance predictions.
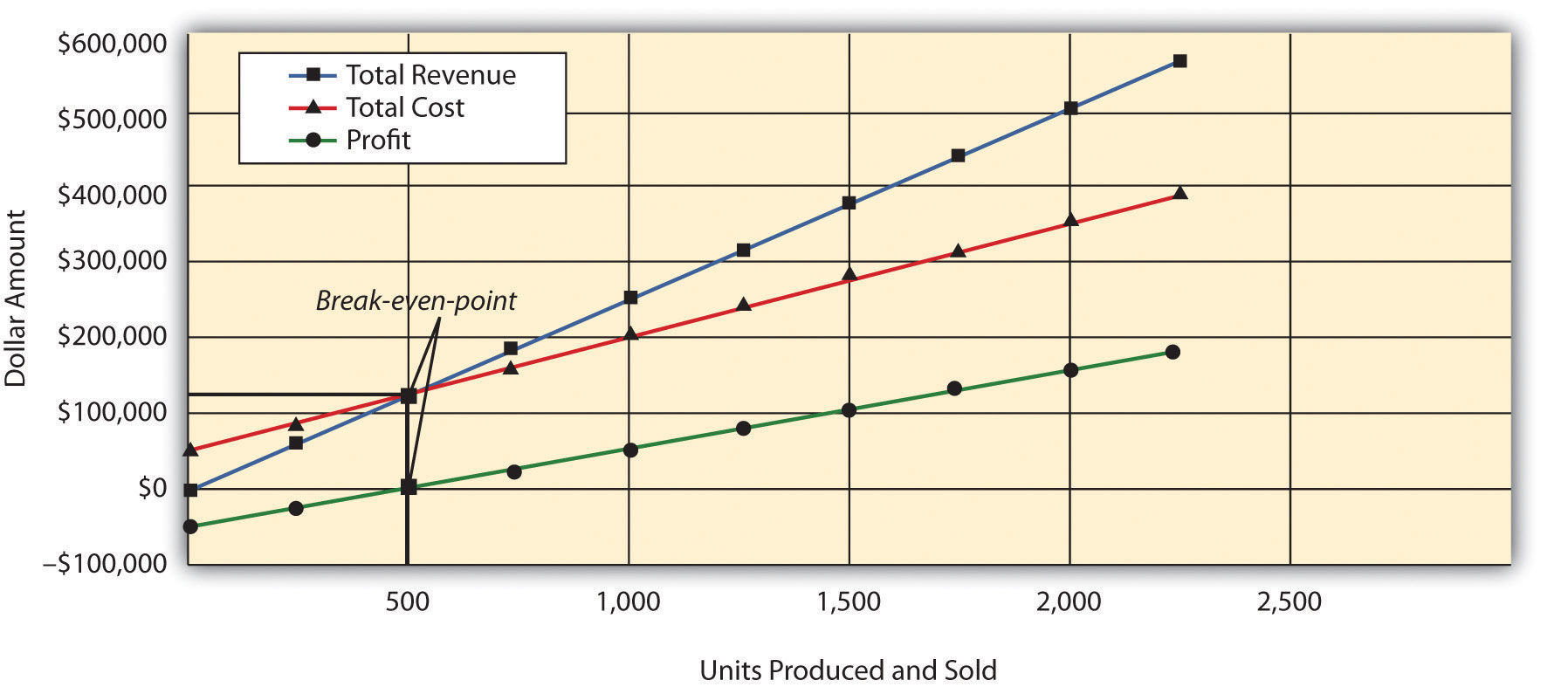
Break-even analysis is a tool that can be used to demonstrate and calculate how much revenue is needed to make a certain amount of profit, assuming expenses remain constant. An organization may use CVP analysis as a planning tool when the management wants to find out the desired profit when the sales volume is known. This can be answered by finding the number of units sold or the sales dollar amount. Cost-volume-profit analysis or CVP analysis, also known as break-even analysis, is a financial planning tool leaders use to create effective short-term business strategies. The most critical input in CVP analysis is the relationship between different costs and volume i.e. the categorization of costs into fixed and variable categories.
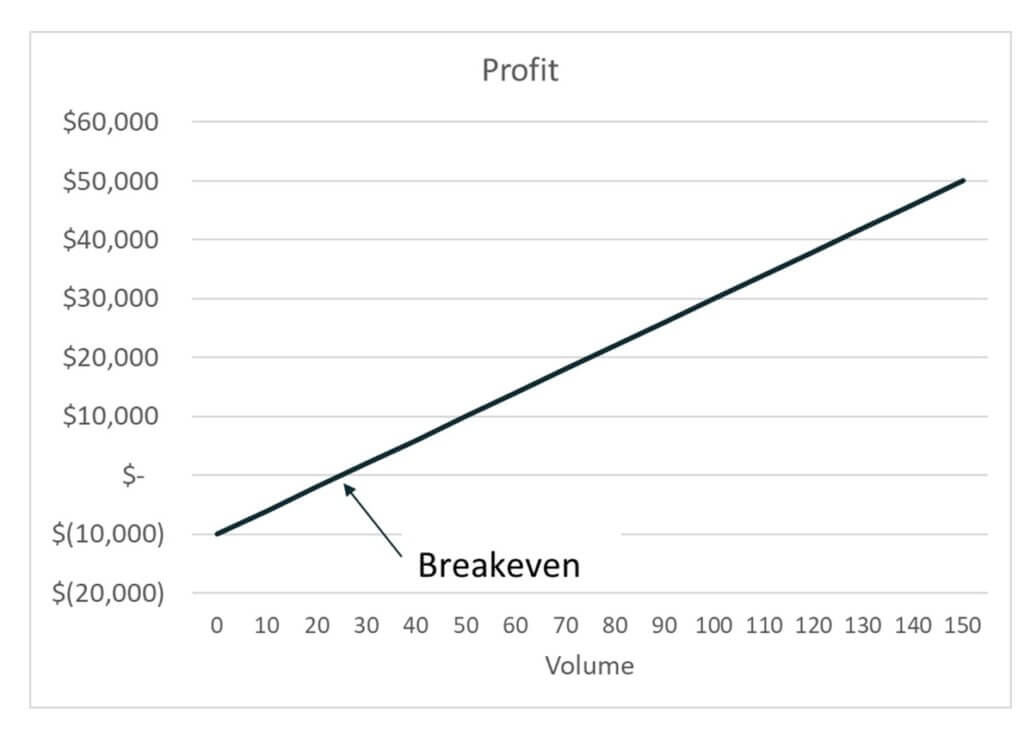
CVP is a comprehensive analysis that examines the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profit to determine break-even points and profit targets. To find out the number of units that need to be sold to break even, the fixed cost is divided by the contribution margin per unit. Whether the sandwich shop sells 50 subs or 50,000 subs, these costs stay the same. In our sandwich business example, let’s say our fixed costs are $20,000. It shows that break-even point can be calculated by dividing fixed cost by the contribution margin per unit.
It provides valuable insights into the financial dynamics of a business. CVP analysis is used to determine whether there is an economic justification for a product to be manufactured. The decision maker could then compare the product’s sales projections to the target sales volume to see if it is worth manufacturing.
